Introduction
Chandrayaan-3, India’s second attempt to land on the Moon, was launched on Friday by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). The nation aims to become the fourth country to achieve this remarkable feat. In this article, we will explore the challenges of lunar exploration, the relevance of this mission, and the goals of Chandrayaan-3.
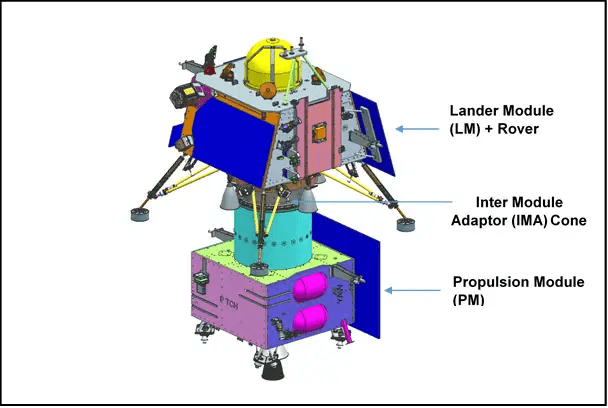
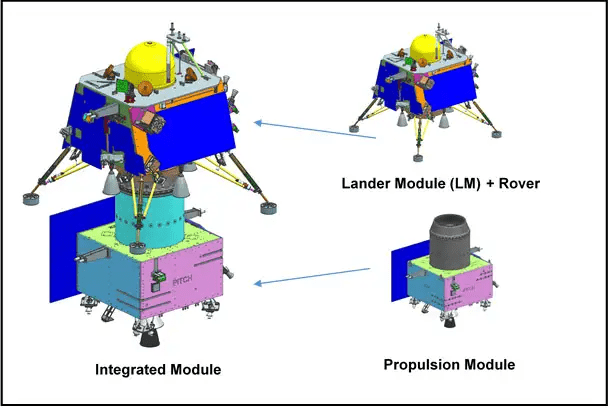
The Elusive Goal of Landing on the Moon
A Prominent Success for Human Exploration
Almost fifty years ago, on July 21, 1969, Neil Armstrong made history by taking the first human step on the Moon, forever changing the course of human exploration. But even today, landing on the Moon successfully remains a very challenging task.
Failed Moon Missions
In 2019, ISRO made its last attempt to land an unmanned spacecraft, Chandrayaan-2, on the lunar surface. Unfortunately, the mission encountered a setback when the Vikram lander crashed into the Moon’s surface during the final stages of landing.
It’s worth noting that other countries also experienced failures in their lunar missions during the same year. Israel’s Beresheet mission and Japan’s Hakuto-R mission faced similar setbacks. These examples highlight the challenges and risks associated with lunar exploration.
Reaching for the Moon
Navigating the Vast Distance
Before attempting to land on the Moon, a spacecraft must first undertake the daunting task of navigating a vast distance of approximately 384,400 kilometers. This long journey presents numerous challenges that must be overcome before approaching the lunar surface.
Entering the Lunar Orbit
To successfully land on the Moon, a spacecraft must enter its orbit. This involves precise calculations and a well-functioning propulsion system. Minor failures during this stage can lead to mission abandonment, as seen in NASA’s case when a spacecraft’s propulsion system failed to enter the lunar orbit.
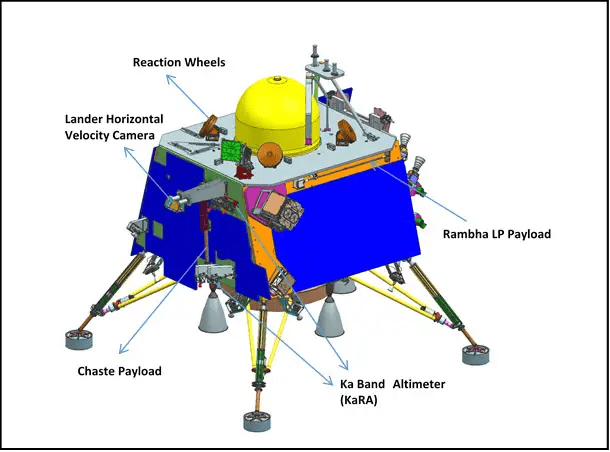
The Challenge of Soft Landing
The “15 Minutes of Terror”
One of the crucial steps in lunar missions is the soft landing, often referred to as the “15 minutes of terror.” During this phase, the lander must fire its engines at the right times and altitudes, consume the proper amount of fuel, and make accurate scans of the lunar surface’s topography. The entire process is autonomous, as real-time guidance from Earth is not possible.
Overcoming the Lack of Atmosphere
Unlike Earth, the Moon lacks a substantial atmosphere that can aid in slowing down a spacecraft for landing. This absence of atmospheric friction requires the lander to decelerate from speeds exceeding 6,000 km/h to zero, making a soft landing a significant challenge.
Lunar Dust and Other Challenges
Even after achieving a soft landing, lunar dust poses additional challenges. When the lander touches down, its thrusters blast lunar dust off the surface at high speeds, potentially obstructing camera lenses and affecting readings. Moreover, the Moon’s uneven surface, filled with craters and boulders, adds complexity to the landing process.
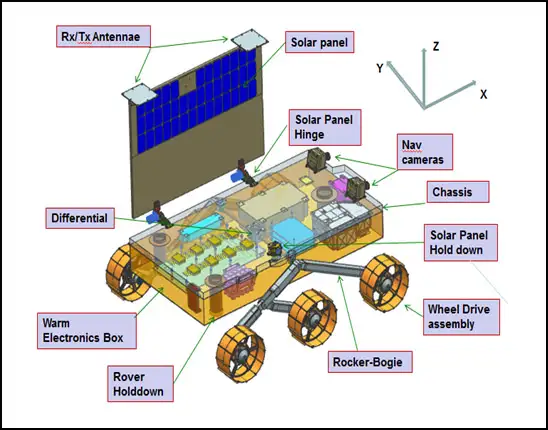
Chandrayaan-3: India’s Pursuit
A Second Attempt at Lunar Landing
Chandrayaan-3 is India’s significant endeavor in space exploration, following the unsuccessful landing of Chandrayaan-2’s Vikram lander in 2019. On Friday, July 14, Chandrayaan-3 was launched from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
Scientific Objectives of Chandrayaan-3
Chandrayaan-3 aims to achieve several objectives, including demonstrating a safe and soft landing on the lunar surface. The mission also intends to showcase the rover’s capability to traverse the lunar terrain and conduct scientific experiments. Notably, Chandrayaan-3 could potentially become the first mission to collect samples of lunar ice formations within craters.
Significance and Expectations
India will join the United States, the Soviet Union, and China as the fourth country to accomplish a soft landing on the Moon if Chandrayaan-3 makes it there. This accomplishment holds immense significance for India’s scientific community and will further enhance the nation’s standing in space exploration.
Chandrayaan-3 is scheduled to land between August 23 and 24, marking a significant turning point in India’s space voyage.
Conclusion
India’s spacecraft, Chandrayaan-3, represents the nation’s dedication to advancing space science as it sets off on its mission to conquer the Moon. Although lunar landing is still a difficult task, the project gains from the insightful lessons learned from earlier failures and the scientific expertise of ISRO.
Chandrayaan-3’s successful soft landing will not only be a historic accomplishment for India but will also increase knowledge of the Moon’s composition and open the door to new scientific findings. The mission serves as a testament to the country’s relentless dedication and the remarkable ingenuity of its scientists.
Credit for Images : ISRO
For complete details visit : https://www.isro.gov.in/Chandrayaan3_New.html
Also Read This : Elon Musk Announces New Business “xAI” to Create ChatGPT Alternative – EXPOSUREEE

